What is cogeneration?
Cogeneration (Combined Heat and Power, CHP) is a high-efficiency technology that allows the simultaneous production of electricity and useful heat from a single fuel source. Unlike traditional power plants, where up to 60% of energy is lost as heat, cogeneration systems capture and utilize this heat for heating, industrial processes, or steam production, increasing overall efficiency up to 90%.
How cogeneration works?
Cogeneration is a key energy efficiency technology that addresses modern energy challenges. Reducing CO₂ emissions and supporting environmental sustainability. Decentralization of energy and the transition to distributed generation. The cogeneration process is based on three main stages:
Natural gas, biogas, or other fuel is used to power a gas engine or gas turbine
The engine drives a generator that produces electricity for on-site use or grid supply.
Waste heat from the engine, exhaust gases, and cooling system is captured and used for heating, hot water supply, or industrial processes.
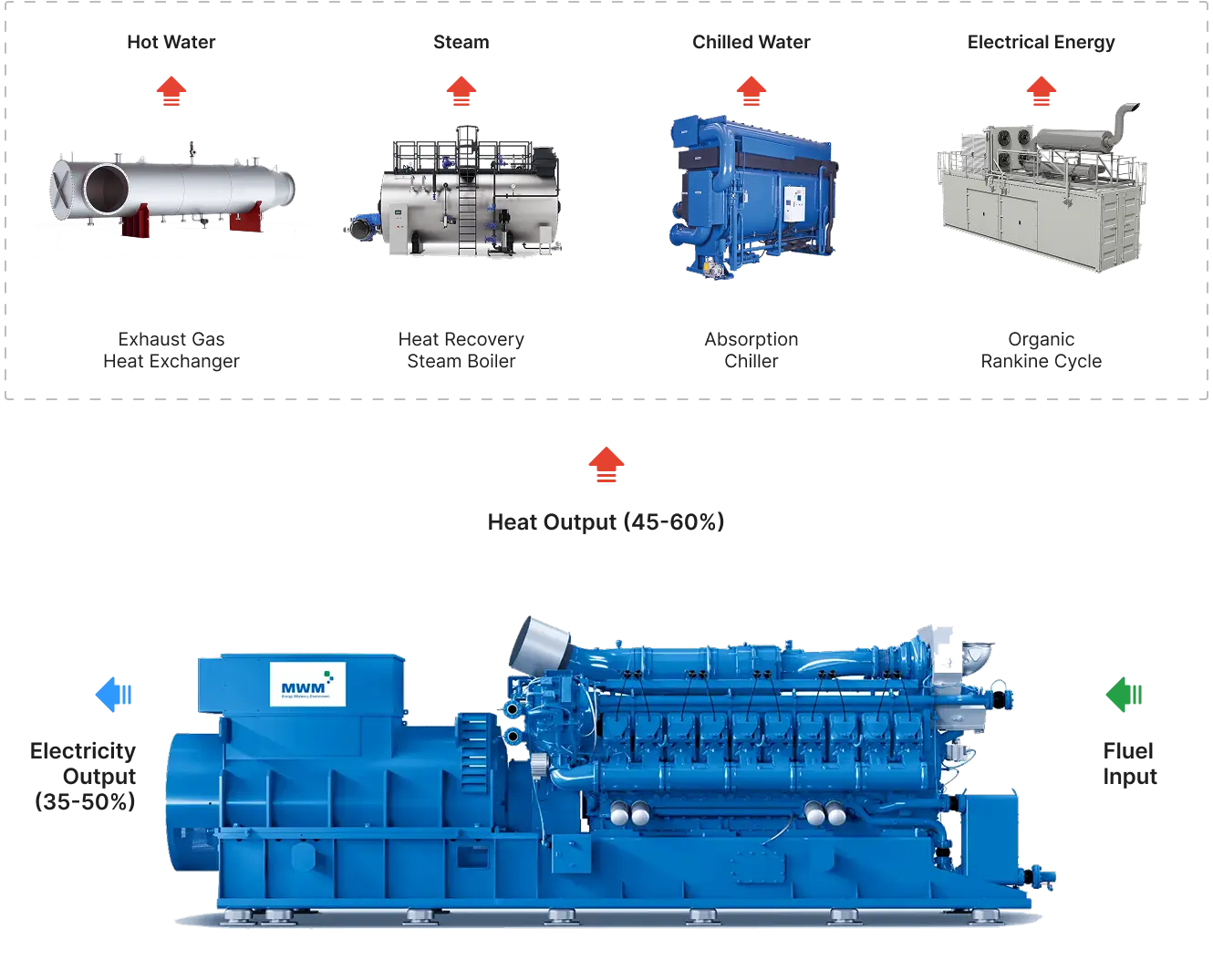
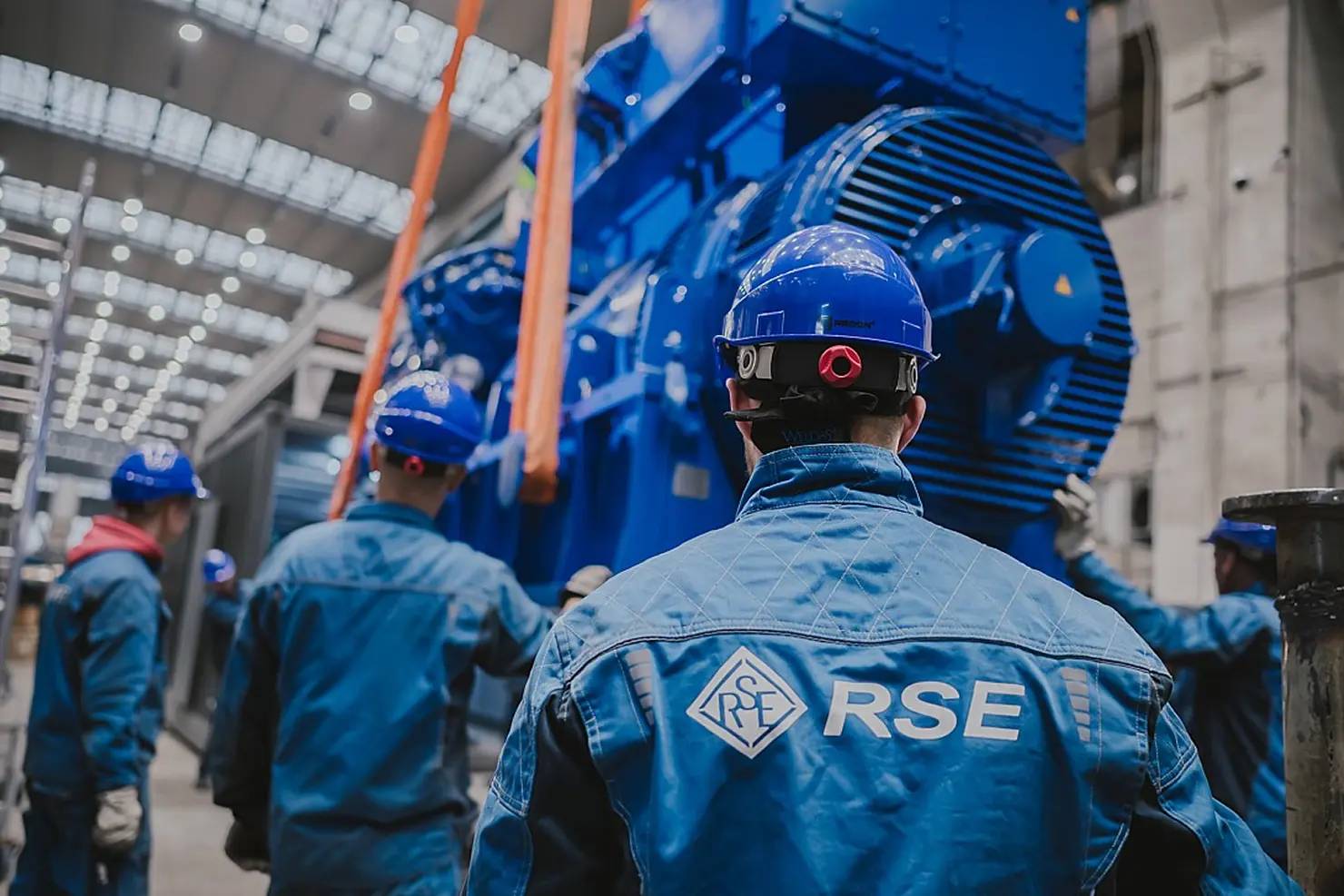
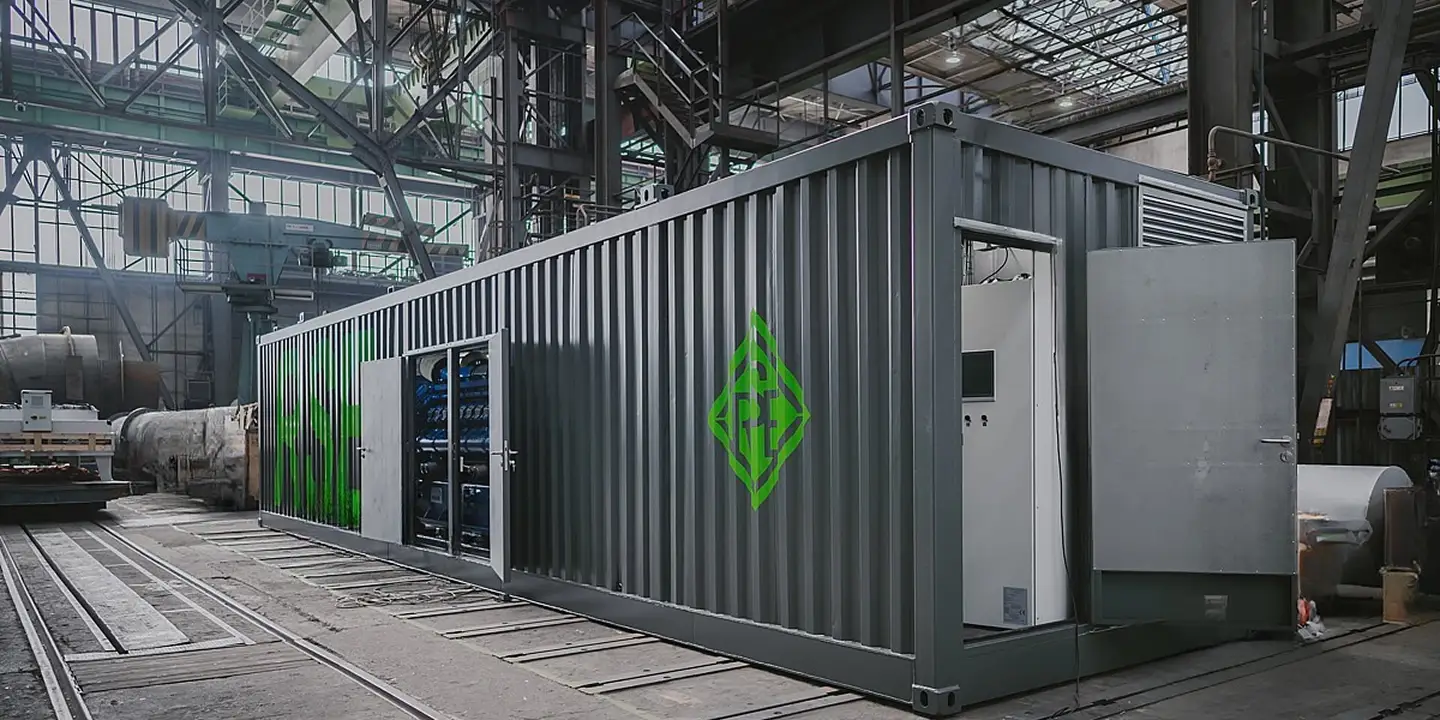
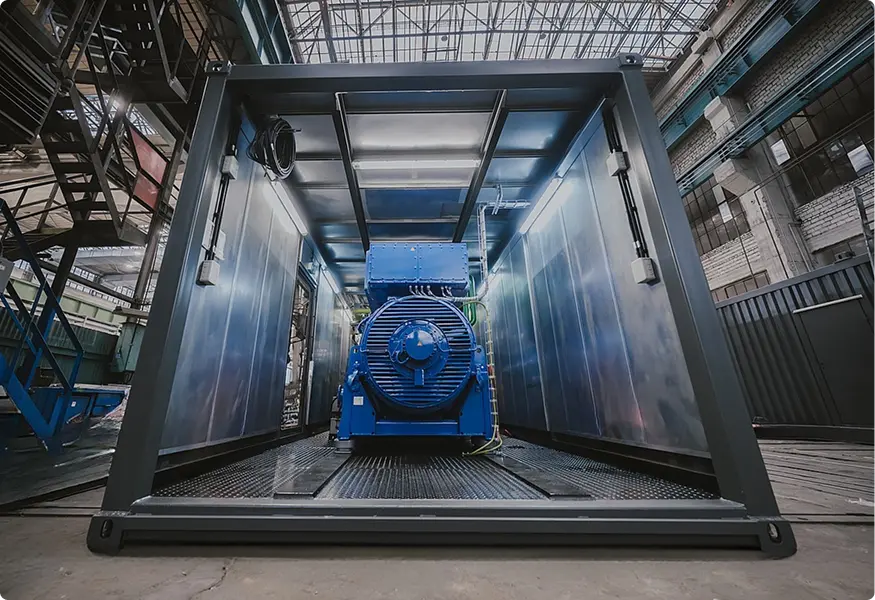
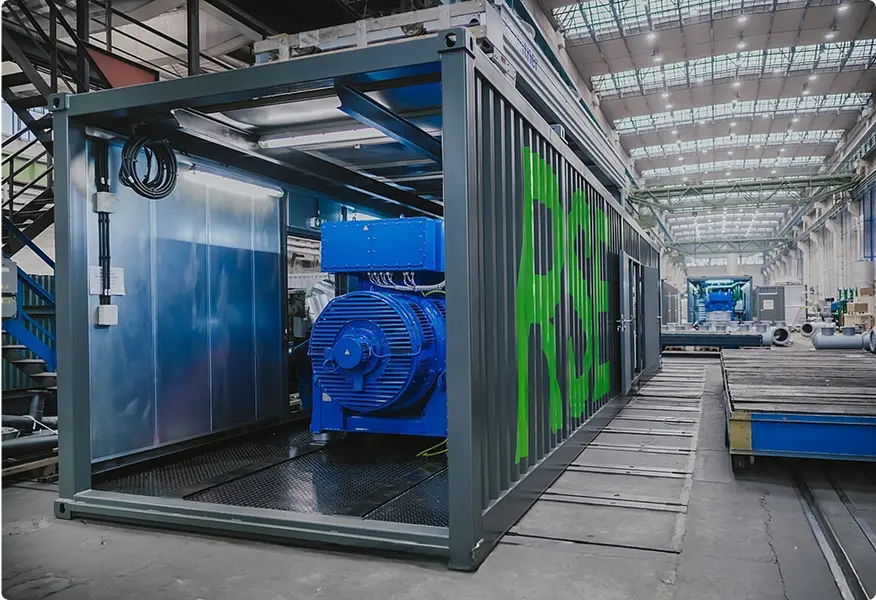
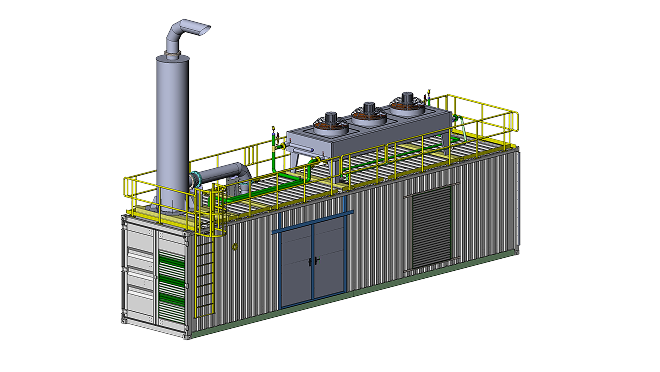
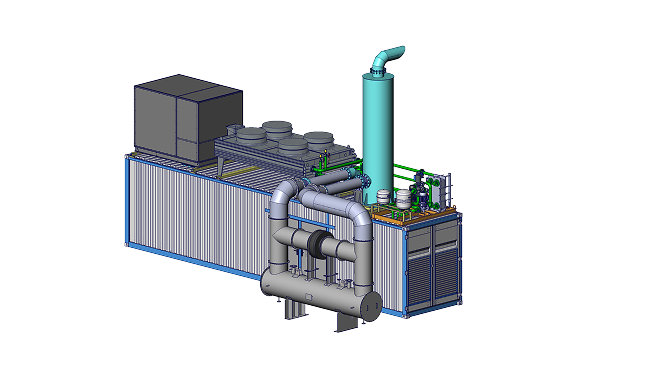
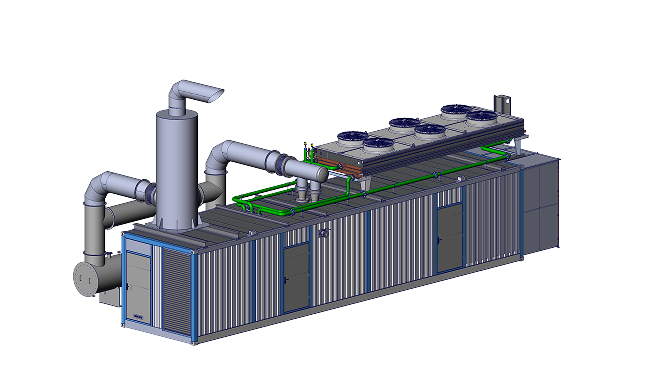
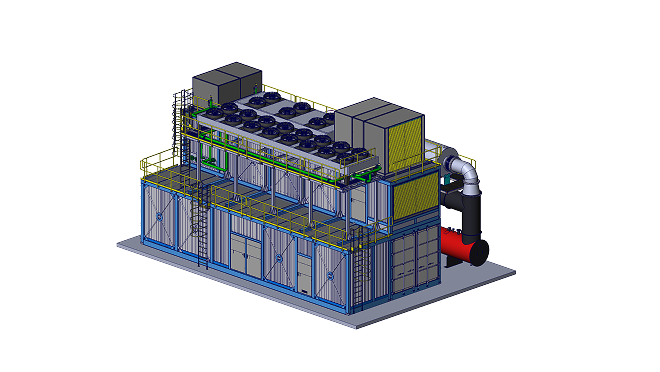
RSE Cogeneration Solutions
Enhancing energy efficiency in industry and the municipal sector. Manufacturing of cogeneration modules in a container design based on MWM gas engines, which ensure continuous work in the production of heat and electricity.
About Modular SolutionsWHY COGENERATION?
Benefits of Cogeneration
Cost Savings
- Reduces electricity costs by up to 40%
- Investment payback in 2-5 years
- Fuel flexibility (biogas, synthetic gas, natural gas, assosiated gas, mining gas, hydrogen)
Environmental & Energy Efficiency
- CO₂ emissions reduction by up to 50%
- Optimal use of primary energy (efficiency up to 90%)
- Less strain on electrical grids and consumption stabilization
Reliability & Autonomy
- Stable power supply with no outages
- Protection from energy crises
- Ability to operate in parallel with the grid or in standalone mode
Cogeneration Power Plant vs
Traditional Power Systems
| Feature | Cogeneration Power Plant | Traditional Power System |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High – up to 80–90% efficiency | Low – around 30–40% efficiency |
| Heat Utilization | Captures and uses waste heat for heating or processes | Waste heat is typically lost to the environment |
| Fuel Usage | Optimized – single fuel source for electricity & heat | Requires more fuel to produce same amount of energy |
| Environmental Impact | Lower CO₂ emissions and reduced environmental footprint | Higher emissions due to energy waste and inefficiency |
| Operating Cost | Lower due to better fuel utilization | Higher due to energy losses and fuel inefficiency |
| System Reliability | High – provides both power and heat, enhancing resilience | Dependent solely on grid or backup systems |
| Application Flexibility | Ideal for industrial, commercial, and district heating | Primarily for large-scale electricity production |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront cost, but long-term savings | Lower initial cost, but higher operating expenses |
TRENDS
Global Cogeneration Trends
Explore solutionsCarbon
Reduction
A worldwide shift is underway to lower CO₂ emissions & accelerate the transition to low-carbon systems.
EU
Green Deal
The European Union aims to cut CO₂ emissions by 55% by 2030, promoting cleaner energy solutions like cogeneration.
Proven Emission Savings
Research shows cogeneration can reduce emissions by 250–600 g CO₂/kWh compared to traditional power generation.
Government
Support
Increasing government funding & incentives are available for Combined Heat and Power (CHP) projects, encouraging wider adoption.
Market
Growth
The Global market is expanding, with an estimated annual growth rate of 6.5%, driven by energy efficiency demands.
RSE & MWM – Partnership for Energy Excellence
Through our partnership with MWM, RSE delivers cutting-edge modular solutions, ensuring energy independence and efficiency for businesses worldwide.
Contact Sales